Table of Contents

Introduction How Western toilets Works
Ever wondered how your toilet does its job? This guide breaks down the parts of your toilet in simple terms, so you can better understand how it all works. Let’s explore the toilet tank, toilet bowl, and the pipes that make it all happen.
A. Inside the Toilet Tank How it’s Work
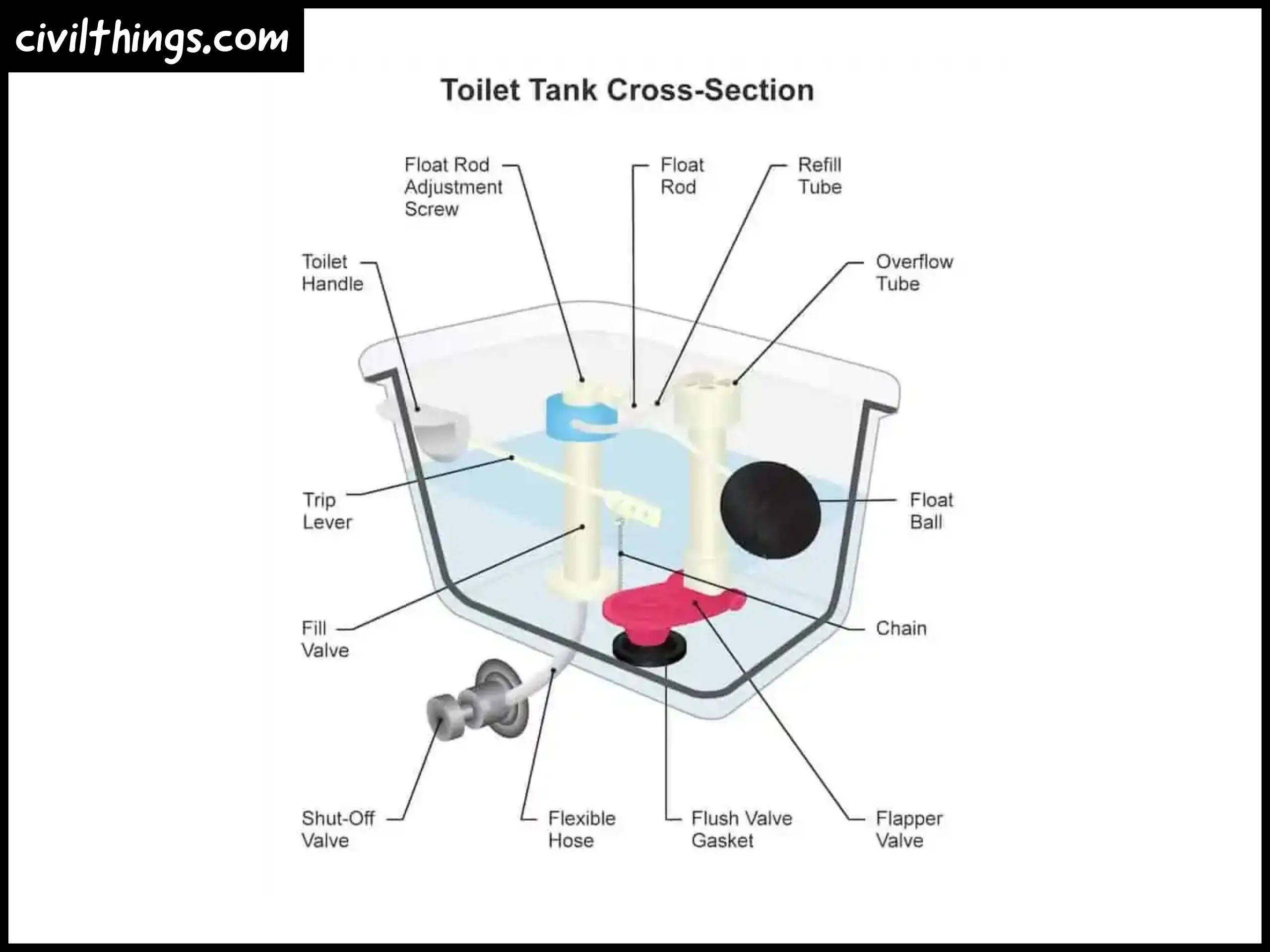
- Toilet Tank Cover: The Lid on the Secrets
This lid keeps the inside of your toilet clean and covers up all the important parts.
- Handle and Trip Lever: The Start of the Flush
When you push or pull the handle, it starts the flushing process. It’s connected to the trip lever.
- Chain and Flapper Valve: Making the Water Go
The chain and flapper valve work together to let water into the bowl when you flush.
- Float and Refill Tube: Keeping the Right Amount of Water
The float and refill tube make sure there’s enough water in the tank for the next flush.
- Overflow Tube and Flush Valve: Stopping Overflow
These parts prevent the tank from getting too full and spilling water everywhere.
- Fill Valve: Putting Water Back In
The fill valve brings water back into the tank after a flush.
B. Understanding the Toilet Bowl how Works
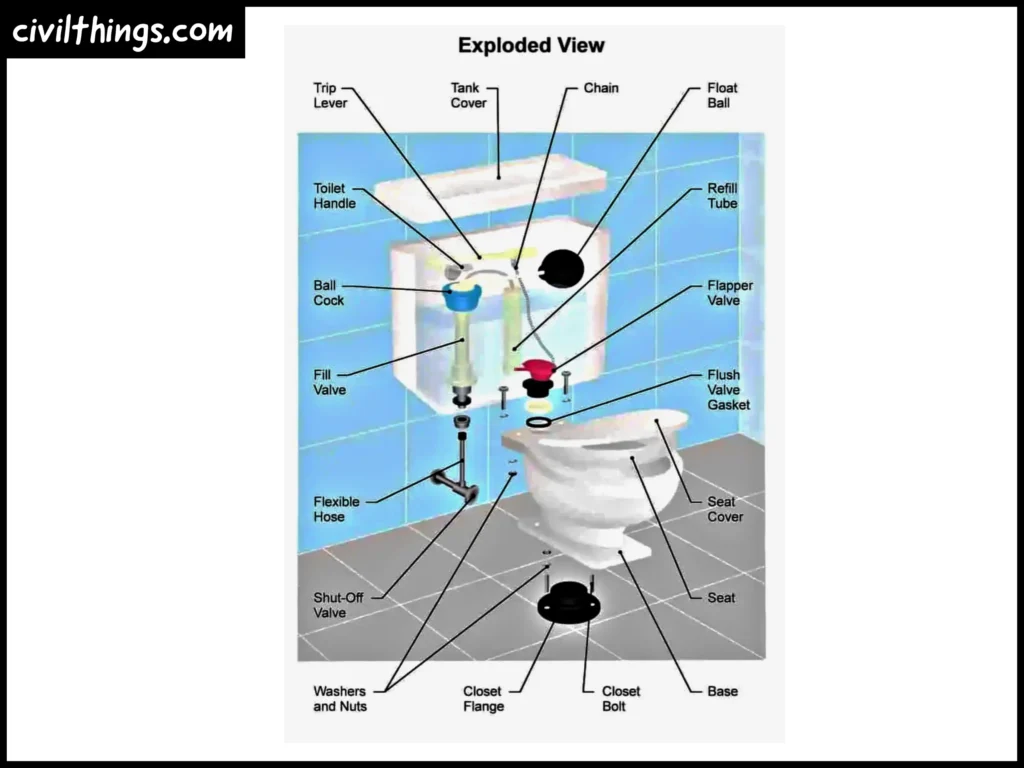
- Lid and Seat: Covers and Comfort
The lid and seat cover the bowl and give you a comfortable place to sit.
- Rim and Rim Holes: Guiding the Water
The rim directs water during a flush, and small holes around the rim let water in.
- Wax Ring and P-trap Pipe: Sealing and Trapping Smells
The wax ring seals the toilet to the floor, and the P-trap pipe stops smells from coming into your home.
- Toilet Flange and Drain Pipe: Connecting and Moving Waste
The toilet flange connects the toilet to the drain pipe, and the drain pipe carries waste away.
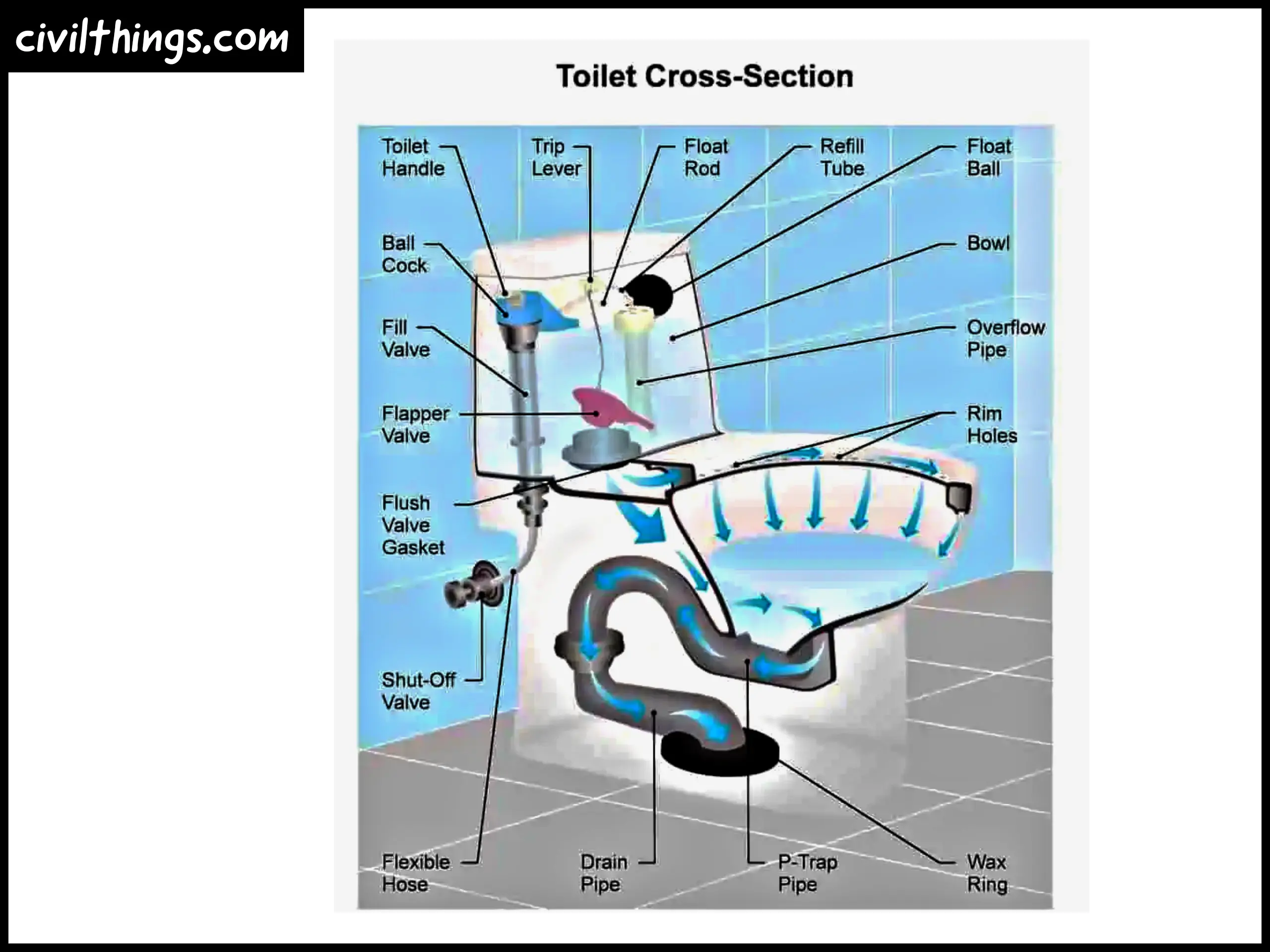
How does a toilet flush system work?
C. Checking Out Plumbing Components
- Water Supply Line: Bringing in Water
This line connects the toilet to the water, so there’s always water for flushing.
- Shut-off Valve: Turning Water On and Off
The shut-off valve controls the water flow to the toilet and helps with repairs.
Conclusion of How Toilets Works
Now you know how your toilet works! With this knowledge, you can understand and fix small problems, and you might even appreciate your toilet a little more. The next time you flush, remember the cool things happening behind the scenes.
How does a toilet work step by step?A
toilet works by using a flush mechanism. When you push the flush handle, it lifts the flapper valve in the tank, allowing water to rush into the bowl, carrying away waste. The tank then refills for the next use.
What is the physics behind a toilet flush?
The flush relies on the force of gravity and the principles of fluid dynamics. When the flush handle is pressed, water from the tank is released into the bowl, creating a siphon effect that efficiently clears the bowl.
How does toilet plumbing work?
Toilet plumbing involves a water supply line, shut-off valve, and a drain pipe. The water supply line fills the tank, the shut-off valve controls water flow, and the drain pipe carries waste away to the sewer or septic system.
What is the process of the toilet system?
The toilet system involves filling the tank with water, initiating a flush when needed, and then refilling the tank for the next use. The waste is carried away through the drain pipe connected to the sewer or septic system.
How does an Indian toilet work?
Indian toilets typically use a trap in the bowl to hold water, and a flushing mechanism to clear waste. Unlike Western toilets, users often squat over the bowl rather than sitting.
What is inside a toilet?
Inside a toilet, you’ll find a tank with components like the flapper valve, float, fill valve, and flush handle. The bowl has a trap, rim, and drain, while the plumbing includes a water supply line and a drain pipe.
How does water stay in a toilet?
Water stays in the toilet bowl due to the design of the trap. The trap retains a certain amount of water to prevent sewer gases from entering the bathroom while maintaining a seal.
Who invented the toilet?
The modern flush toilet was invented by Sir John Harington in 1596. However, the flushing toilet as we know it today was popularized by Thomas Crapper in the late 19th century.
Where does toilet waste go?
Toilet waste is carried through the drain pipe and into the sewer or septic system, eventually reaching a wastewater treatment plant or a septic tank for processing.
Do toilets need water?
Yes, toilets require water for proper functioning. Water is essential for flushing waste and maintaining the trap seal that prevents sewer gases from entering your home.
How do toilets connect to the sewer?
Toilets are connected to the sewer through the drain pipe. The drain pipe carries waste from the toilet to the sewer or septic system for proper disposal.
Keywords
Toilet Parts, How Toilets Work, Toilet Tank, Toilet Bowl, Plumbing, Toilet Mechanism, Toilet Repair, Toilet Maintenance, Simple Toilet Explanation, Toilet Guide.
Important Post
Top 12 Steps Used in Construction Process
Best Methods of Terrace Waterproofing & Roof in Detail
Structural Audit – Objectives | Bye-Laws | Importance
Surveying and Types of Compass

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!

Comments are closed.