Type of Contract is a very important part Contract and Accounts of civil engineering. it’s very important subject in diploma & degree and following points are very important to exam point of view must read and understand properly it’s help you all the best.
Contract Introduction:
Contracts play an important role in our everyday life. Even without realizing it, we enter into a contract, for example, when one enters a vacant taxi and asks the driver to take to his destination he has entered into an ‘implied contract’. The driver agrees to take that person to his destination for the payment to be made to him as shown by the taxi meter. All such transactions in our everyday life are based on agreements that create mutual rights and obligations.
The principles of the contract are laid down in sections 1 to 75 of ‘The Indian Contract Act 1872.
Also Read,
AIR POLLUTION – DEFINITION | EFFECT | CONTROLLING
TYPE OF WATER INTAKE STRUCTURES | WORKING | NOTES
Tehri Dam – Photos | Construction Details | Location
Why AAC Blocks are a Smart Choice for Construction
LONGEST NATIONAL HIGHWAYS IN INDIA
Definition of Contract:
A contract is an undertaking by a person or firm to do any work under certain terms and conditions.
The work may be for construction maintenance and repairs for the supply of materials, labor, transport of materials, etc.
Objects of contract.
- To efficiently carry out tasks by the agreed-upon terms and specific requirements.
- To have a free hand for a supervisor to check the work done by the contractor without interference.
- To execute the work by the experienced engineer.
- To use machinery and the latest techniques in execution.
Requirement of Valid contract :
1. Contracts in writing
2. Subject Matter
3. Can be enforced in a court of law
4. Parties must be competent
5. Free consent of parties
6. Attested by the witness
1. Contracts in writing:-
According to the law, the contract should be in writing and should be signed by both parties. In the case of a joint partnership, the name of the partner is written and signed by only one partner who is having a power of attorney to sign the document. In the case of the Government Department, the officer is duly authorized to sign the contract on behalf of the department.
2. Subject Matter:
The subject matter of the contract must be legal & definite.
3. Can be enforced in a court of law:
All the conditions should be according to law because the court can force only such conditions.
4. Parties must be competent :
As per the Indian Contract Act, the parties signing the document should be legally competent.
5. Free consent of parties :
Both the parties to the agreement must give their free consent. The parties must agree to the same thing in the same sense.
6. Attested by witness :
The signature of both parties should be attested by another responsible person or officer.
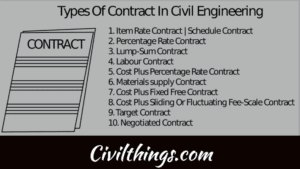
Types of Engineering Contracts
The following are different types of contracts.
- Lump sum contract
- Item rate contract
- Percentage rate contract.
a. cost plus percentage rate contract.
b. cost plus fixed fee contract.
c. cost plus variable fee contract.
d. cost plus variable percentage. - Labor contract.
- Demolition contract
- Fee contract.
- Target contract.
- Negotiated contract.
- Material supply contract.
1. Lump sum contract:
In a Lump-sum contract, the contractor undertakes the execution or construction of a specific work with all its contingencies, to complete it in all respects within the specified time for a fixed amount. The detailed specification of all items of work about the whole work plans and detailed drawings, and deposit of 10% security money, penalty, progress, and other conditions of the contract are included in the contract agreement.
The general specification and description of different parts of a building with dimensions where required are included.
The quantities or schedules of different items of work are not provided. The contractor shall have to complete the work as per plan and specification, within the contract fixed sum, within a fixed time, irrespective of quantities of different items.
If, in a lump-sum contract, an extra item crops up, it is adjusted in any one of the following ways.
1. If the extra item is substantial, fresh tenders may be invited for the same.
2. The rate of the extra item may be determined from the schedule of rates if any.
3. The amount of the extra item may be paid on a day-work basis.
4. The amount of the extra item may be worked out by adding a fixed percentage of a fixed lump-sum amount to the actual cost of the extra item.
Advantages:-
1. Total cost of the project is known before the completion of work.
2. Employment of staff to maintain accounts is not necessary.
3. The contractor can derive greater profit through proper planning.
4. Early completion of work.
5. As it is a lump-sum contract, the measurement of works will be restricted only to the extra items, thus reducing the burden of measurements.
Disadvantages:-
1. This type of contract may become unbalanced because the contract may result in excess profit or loss to the contractor.
2. Disputes occur between owner and contractor.
3. Quality of work is not guaranteed and it is a risk for the contractor.
Item rate contract method:-
It is also known as a unit price contract or schedule contract.
Within this context, contractors must provide rate quotations for each work item based on the schedule of quantities provided by the department. This comprehensive schedule encompasses the complete vocabulary of items as specified in the approved estimate, estimated quantities, and their respective units. The rates quoted by the contractor are inclusive of material, labor, tools and plants, overhead charges, and contractors’ profit. The actual quantities may be more or less than the estimated quantities but the rate of the item remains fixed.
While filling up the rates, the contractors are required to express the amount in figures and words and also to work out the cost against each item.
This type of method is followed for most of the public works executed by the Government and also by the Railway Department. Also, this type is suitable for buildings, roads, bridges, etc.
Advantages:
1. The contractor is paid based on the actual quantity of work that will be carried out, the method may prove to be economical.
2. There are no chances of excessive profit or loss to the contractor and hence it is a balanced one.
3. In this type of contract, the contractor tries to complete the work as early as possible to utilize the tools and plants, etc. on some other work.
4. It allows for any extra items.
5. There is no risk hence the quality of work is assured.
6. In this possibility of variations in items of work due to variations in plans.
Disadvantages:
1. Exact cost of work to be executed is not known to start with.
2. Payment is to be given to the contractor as per measurements, thus workload of the Architect/Engineer is considerably increased.
3. Both owner and contractor to appoint staff for taking measurements and to prepare bills.
4. Possibility of contractor submitting an unbalanced tender.
difference between item rate contract and percentage rate contract
Difference between lump-sum contract and item rate contract.
| Sr.N | Item Rate Contract | Lump Sum Contract |
| 1 | In this type of contract, there is no chance of excessive profit or loss to the contractor and hence it is balanced. | This type of contract may become unbalanced because the contract may result in excess profit or less to the contractor. |
| 2 | The total cost of work is not known at the start. | The total cost of the project is known before the completion of work. |
| 3 | The total cost of work is not known at the start. | Quality of work is not guaranteed and it is a risk for the contractor. |
| 4 | It allows for any extra items. | The measurements of works will be restricted only to the extra items. |
| 5 | Both owner and contractor appoint staff for taking measurements and to prepare bills. | The employment of staff to maintain accounts is not necessary. |
FAQ:
Q1.Define ‘Contract’.
Q2.Enlist object of Contract.
Q3.Write down the requirement of valid-contract.
Q4.Explain the requirement of valid-contract.
Q5.List different types of engineering contracts.
Q6.Explain the lump sum contract in detail.
Q7.State the advantages of disadvantages of item rate contracts.
Q8.Difference between lump sum contract and item rate contract.

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!