Table of Contents
What Is the Critical Path in Project Management?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that identifies the sequence of essential tasks that determine the project’s duration. Understanding what the critical path is in project management helps in planning, scheduling, and controlling complex projects. This method is crucial for ensuring timely project completion and efficient resource allocation.
What Is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
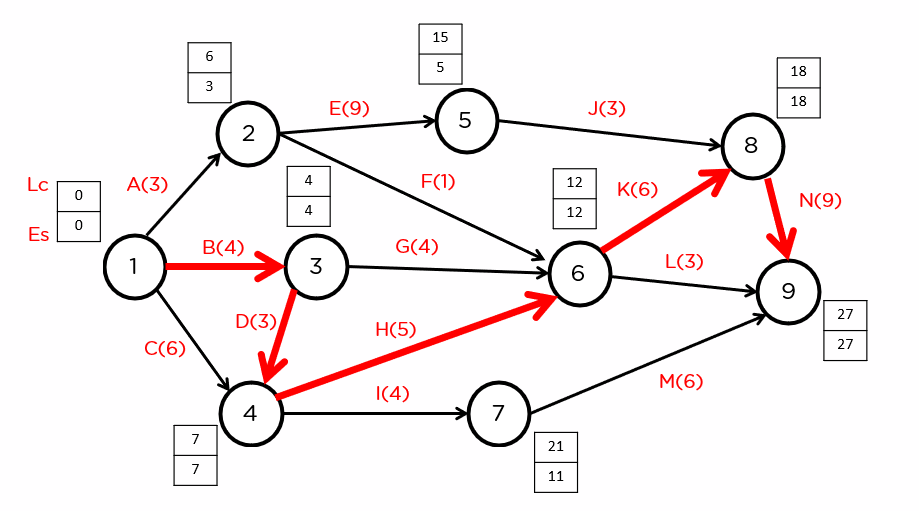
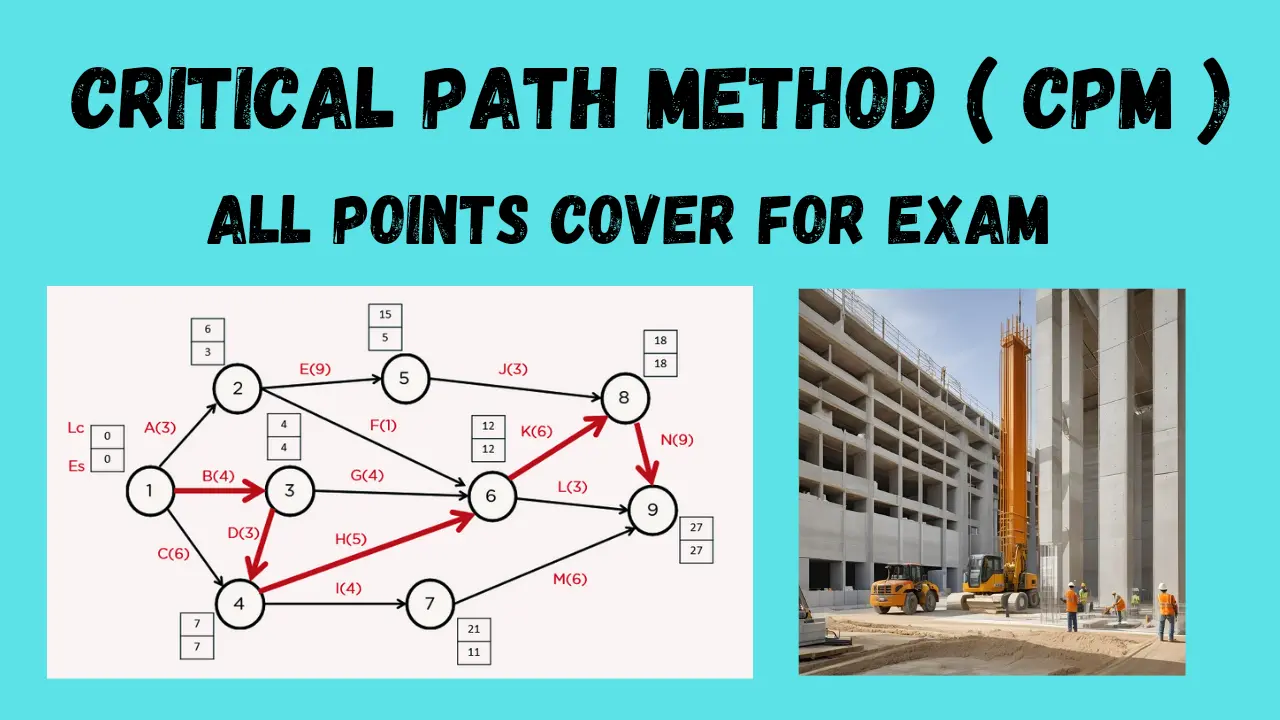
CPM is a step-by-step project management technique for process planning. It calculates the minimum completion time for a project by identifying the longest sequence of dependent activities. This sequence is known as the critical path, and it determines the shortest possible duration for the entire project.
CPM vs. PERT
Both CPM and PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) are project management tools, but they differ in focus:
- CPM is deterministic and used for projects with well-known activities.
- PERT is probabilistic and used for projects with uncertain activity durations.
When Should You Use Critical Path Analysis?
Critical Path Analysis is beneficial for:
- Complex projects with interdependent tasks.
- Projects with tight deadlines.
- Projects requiring efficient resource management.
What Is the Importance of CPM in Project Management?
The importance of CPM in project management includes:
- Timely Completion: Identifies critical tasks that need attention to avoid delays.
- Resource Optimization: Helps allocate resources efficiently.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential bottlenecks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CPM
| Advantages ✅ | Disadvantages ❌ |
|---|---|
| Provides a clear project timeline. | Can be time-consuming to implement. |
| Identifies critical tasks to prevent delays. | Requires accurate data and estimates. |
| Helps in resource optimization. | Complex for large projects with many tasks. |
| Improves project planning and scheduling. | May overlook non-critical tasks. |
| Assists in risk management. | Requires continuous updates and monitoring. |
| Enhances communication among team members. | Depends heavily on project management software. |
| Facilitates project tracking and monitoring. | Limited flexibility for changes once started. |
| Supports decision-making processes. | Can be costly to maintain. |
| Enables effective deadline management. | May require specialized training. |
| Reduces project costs through efficient planning. | Potential for human error in data input. |
Critical Path Method (CPM) Formula
The CPM formula involves:
- Earliest Start Time (EST)
- Earliest Finish Time (EFT)
- Latest Start Time (LST)
- Latest Finish Time (LFT)
The formula helps calculate the slack time for each activity.
Critical Path Method Example
Consider a project with activities A, B, C, and D:
- A (Duration: 2 days)
- B (Duration: 4 days, depends on A)
- C (Duration: 3 days, depends on A)
- D (Duration: 2 days, depends on B and C)
The critical path is A -> B -> D, with a total duration of 8 days.
Critical Path Method Steps
Steps to implement CPM:
- List Activities: Identify all tasks.
- Sequence Activities: Determine task dependencies.
- Draw the Network Diagram: Create a visual representation.
- Estimate Activity Duration: Assign time estimates.
- Identify the Critical Path: Calculate the longest path.
Benefits of Using CPM in Project Management
Key benefits of CPM include:
- Improved Planning: Clear timelines and task sequences.
- Efficient Scheduling: Optimal resource use.
- Better Monitoring: Track progress and identify delays.
How to Draw a CPM Network
📝Step 1: List all Activities
Begin by listing all the activities involved in the project. Each activity should have a unique identifier and a description.
🔗Step 2: Determine Dependencies
Identify the dependencies between activities. Determine which activities must be completed before others can start.
⚪Step 3: Draw Nodes for Each Activity
Draw a node (usually a circle) for each activity. Label each node with the activity identifier and duration.
➡️Step 4: Connect Nodes with Arrows
Connect the nodes with arrows to represent dependencies. An arrow from node A to node B means activity A must be completed before activity B can start.
⏩Step 5: Calculate Early Start and Finish Times
Calculate the early start (ES) and early finish (EF) times for each activity, starting from the beginning of the project and moving forward.
⏪Step 6: Calculate Late Start and Finish Times
Calculate the late start (LS) and late finish (LF) times for each activity, starting from the end of the project and moving backward.
🔍Step 7: Identify the Critical Path
Identify the critical path by finding the longest path from the start to the end of the project. The critical path has zero float (total slack).

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!