Table of Contents
A staircase is not just a movement path between floors—it is a structural element that safely transfers loads to beams, slabs, and columns. For fresh civil engineers and site trainees, understanding staircase reinforcement is often confusing because it involves geometry, load transfer, detailing, and site execution together.

This blog is written in simple English, with a practical, human touch, so that freshers, diploma students, and B.Tech civil engineers can clearly understand staircase reinforcement details from drawing to site execution.
🧱 What is Staircase Reinforcement?

Staircase reinforcement refers to the steel bars placed inside an RCC staircase to resist:
- Bending moment
- Shear force
- Temperature stress
- Live load from people
- Self-weight of concrete
In simple words, steel bars give strength to concrete stairs, because concrete is weak in tension.
👉 Without proper staircase reinforcement design, stairs may crack, sag, or even fail.
❓ Why Staircase Reinforcement is Important?
Understanding why staircase reinforcement is provided helps freshers remember detailing rules easily.
Key Reasons:
- Concrete is weak in tension
- Staircases act like inclined slabs
- Heavy foot traffic creates bending stress
- Load transfers to landing beams and columns
- Safety of users depends on stair strength
⚠️ Poor staircase reinforcement details can lead to:
- Cracks near landing
- Deflection of waist slab
- Unsafe vibration while walking
📍 Where is Staircase Reinforcement Used?
Staircase reinforcement is used in:
- Residential buildings
- Commercial complexes
- Hospitals
- Schools & colleges
- Industrial buildings
- Duplex houses
- Row houses
Whether it is dog-legged staircase, open well staircase, or cantilever staircase, staircase reinforcement is mandatory.
🏗️ Types of RCC Staircases (Basic Knowledge)
Before learning staircase reinforcement details, freshers must know types of staircases.
| Staircase Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Dog-legged staircase | Most common, no open well |
| Open well staircase | Central opening |
| Straight flight staircase | Single direction |
| Cantilever staircase | Steps fixed at one end |
| Spiral staircase | Circular and compact |
Each type needs different staircase reinforcement design logic.
📐 RCC Staircase Section Explained (Section-AA & Section-BB)
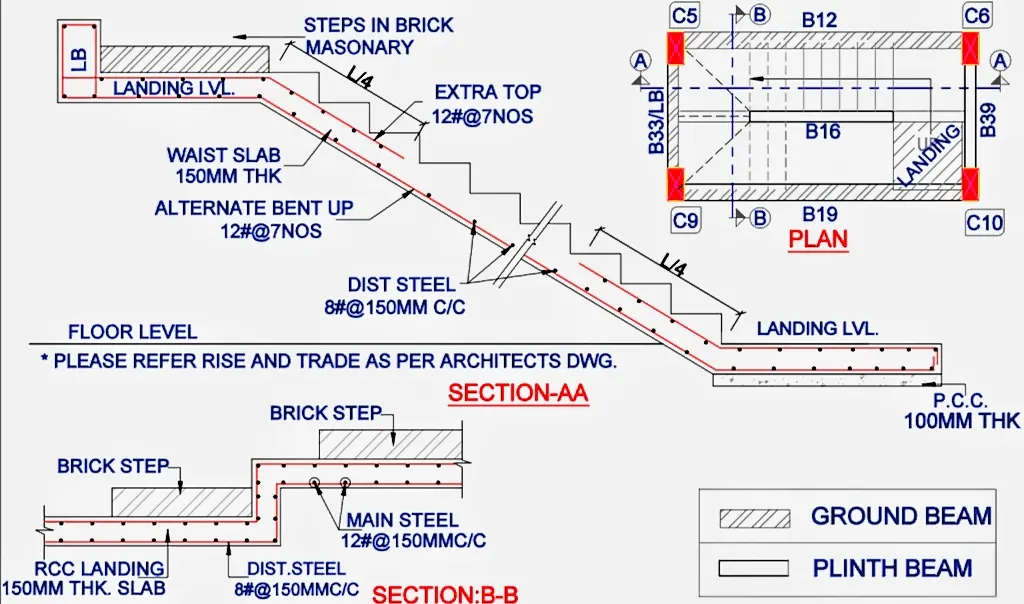
A RCC staircase section shows how steel is placed inside concrete.
Main Components:
- Waist slab (typically 150 mm thick)
- Main reinforcement (along slope)
- Distribution steel (across width)
- Landing slab reinforcement
- Extra top bars near landing
📌 From the image:
- Main steel: 12 mm @ 150 mm c/c
- Distribution steel: 8 mm @ 150 mm c/c
- Extra bars near landing support
This is a standard staircase reinforcement detail followed on Indian sites.
🧮 Staircase Reinforcement Design (Basic Concept)
Load Consideration:
- Self weight of waist slab
- Weight of steps
- Live load (3–5 kN/m²)
- Finish load
Design Concept:
- Staircase acts like simply supported slab
- Main tension develops at bottom
- Extra top bars near supports
👉 Actual calculations are done as per IS 456, but on site, approved drawings are followed.
🧱 Actual Stair Reinforcement at Site (Practical View)
For freshers, actual stair reinforcement looks different from textbooks.
Site Execution Steps:
- Fix shuttering for waist slab
- Mark landing level
- Place bottom main bars
- Provide distribution bars
- Bend extra top bars near landing
- Maintain clear cover (20–25 mm)
- Check bar spacing and anchorage
🛠️ Always cross-check with Bar Bending Schedule (BBS)
👉 You can use this free guide:
🔗 Bar Bending Schedule (BBS): Step-by-Step Guide + Download Excel
https://civilthings.com/download-bbs-excel-sheet-free/
High accuracy BBS calculation tool ( easy cutting length )
🧾 Staircase Reinforcement Details (Standard Practice)
Typical Reinforcement Details:
| Element | Reinforcement |
|---|---|
| Waist slab thickness | 150 mm |
| Main steel | 10–12 mm @ 150 mm c/c |
| Distribution steel | 8 mm @ 150 mm c/c |
| Landing slab | Same as floor slab |
| Extra bars | At top near landing |
These staircase reinforcement details may vary based on span and load.
🏠 Concrete Stairs Design – Simple Explanation
Concrete stairs design focuses on:
- Rise (150–175 mm)
- Tread (250–300 mm)
- Comfortable slope
- Proper landing width
- Adequate reinforcement
📌 Architect decides rise & tread, structural engineer designs staircase reinforcement.
👷 Who is Responsible for Staircase Reinforcement?
| Person | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Structural Engineer | Staircase reinforcement design |
| Site Engineer | Execution as per drawing |
| Contractor | Steel cutting & fixing |
| Supervisor | Quality & spacing check |
| Fresher Engineer | Measurement & inspection |
Freshers must learn drawings + site execution together.
📊 Common Mistakes Freshers Should Avoid
❌ Wrong bar spacing
❌ Missing extra top bars
❌ Poor anchorage into beam
❌ Inadequate cover
❌ Ignoring drawing notes
Always read general notes in staircase reinforcement details.
🔗 Helpful Internal Resources (Use During Learning)
While learning staircase reinforcement, these tools help freshers:
- Row House Construction Estimation Excel Sheet
https://civilthings.com/download-row-house-estimation-excel-sheet/ - Microsoft Excel for Estimation & Costing
https://civilthings.com/microsoft-excel-free-download-for-pc/ - ETABS Software for Structural Design
https://civilthings.com/etabs-software-free-download-for-windows-10/ - STAAD Pro Software Download
https://civilthings.com/staad-pro-software-free-download-2025/ - Revit Software for Civil Engineers
https://civilthings.com/download-revit-software-for-civil-engineering/
🌍 External References (Authority Sources)
- IS 456: Plain and Reinforced Concrete – BIS
- Engineering drawings & detailing references from civil engineering textbooks
❓ FAQs – People Also Ask (Google)
Q1. What is staircase reinforcement?
Staircase reinforcement is steel provided inside RCC stairs to resist bending and ensure safety.
Q2. Which steel is used in staircase reinforcement?
Generally 10 mm or 12 mm bars are used as main reinforcement and 8 mm as distribution steel.
Q3. What is waist slab in staircase?
Waist slab is the inclined slab that supports stair steps.
Q4. How thick is RCC staircase slab?
Usually 150 mm, but it depends on span and design.
Q5. Why extra bars are provided near landing?
Extra bars resist negative bending moments near supports.
🏁 Conclusion
Understanding staircase reinforcement details for freshers is a must-have skill for every civil engineer. Staircases look simple, but structurally they behave like inclined slabs, requiring proper reinforcement design, detailing, and execution.
By learning:
- Staircase reinforcement design
- RCC staircase section reading
- Actual stair reinforcement at site
- Concrete stairs design basics
Freshers can confidently handle site responsibilities and drawings.
👉 Always remember: Good staircase reinforcement means safe movement for generations.
-

How to Calculate Development Length (Ld) When It’s Not Mentioned in Drawing
-

Staircase Reinforcement Details for Freshers (Complete Practical Guide)
-

The Ultimate Guide to Precast Drain and U-Drain Systems: Efficiency in Modern Drainage
-

Drywall Partition | Types, Construction & Cost-Saving Tips 2025

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!
