Table of Contents
PSC stands for Prestressed Concrete is a structural material that has been pre-tensioned or post-tensioned to introduce internal stresses before it is subjected to external loads. This process improves its performance under service conditions. Here’s a detailed look at the concept of prestressed concrete
PSC Full Form in Civil Engineering or Construction is Pre-stressed concrete
1. Basic Principle of Pre-stressed concrete
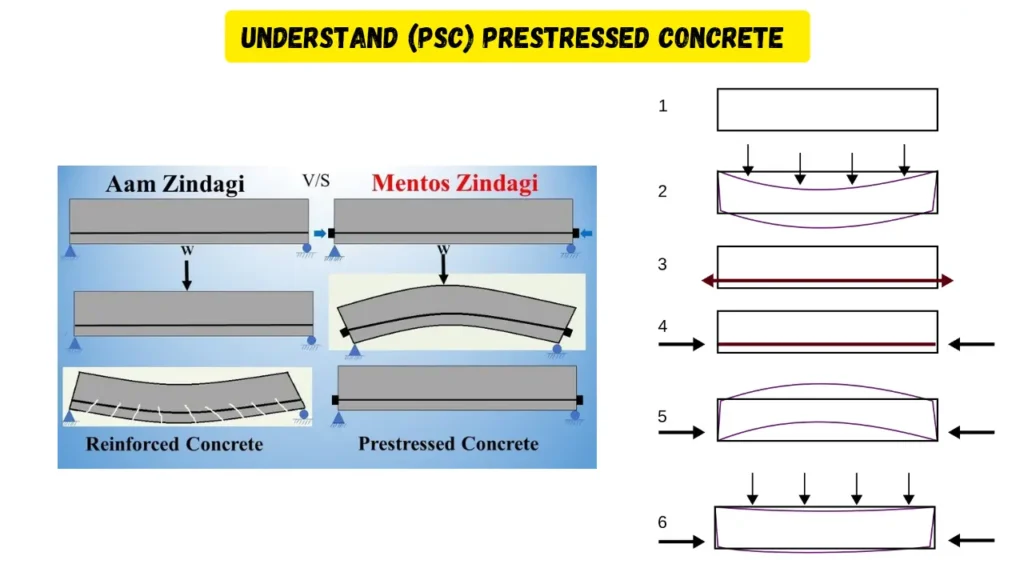
The core idea behind prestressed concrete is to counteract the tensile stresses that occur under load by inducing compressive stresses within the concrete. Concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension. By pre-stressing, the tensile forces are counterbalanced, resulting in an overall improvement in structural behavior.
2. Methods of Prestressing
There are two main methods of prestressing concrete:
a. Pre-tensioning
- Process: In pre-tensioning, the steel tendons (cables or wires) are stretched and anchored to an external frame before the concrete is poured. Once the concrete hardens, the tendons are released, transferring the stress to the concrete.
- Applications: Pre-tensioning is commonly used in factory settings for mass production of items like beams, slabs, and railway sleepers.
b. Post-tensioning
- Process: In post-tensioning, the concrete is cast with ducts or sleeves through which the tendons are threaded. Once the concrete has gained sufficient strength, the tendons are tensioned using hydraulic jacks and anchored against the concrete.
- Applications: Post-tensioning is often used on-site for large structures like bridges, buildings, and parking structures.
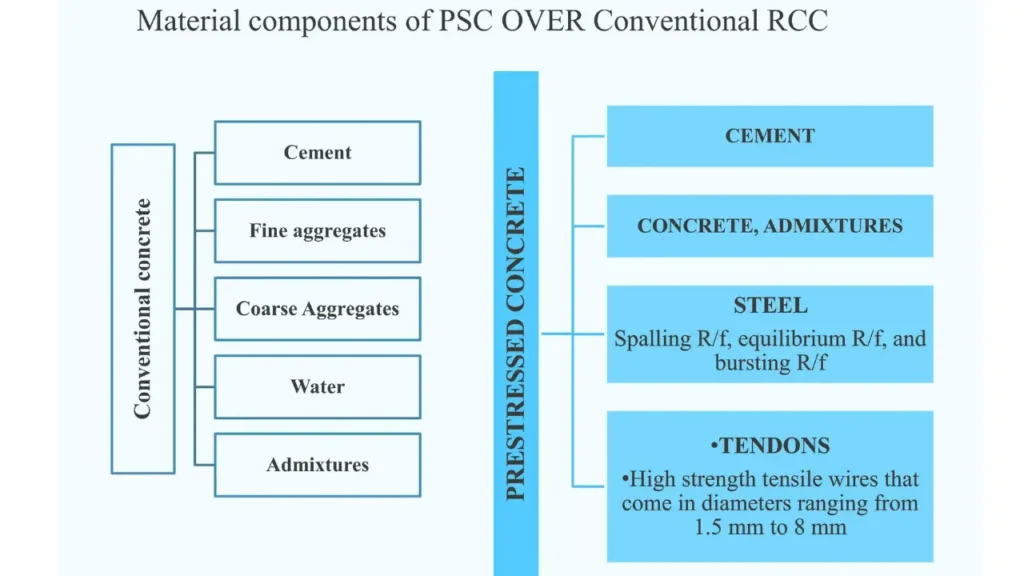
3. Components of PSC
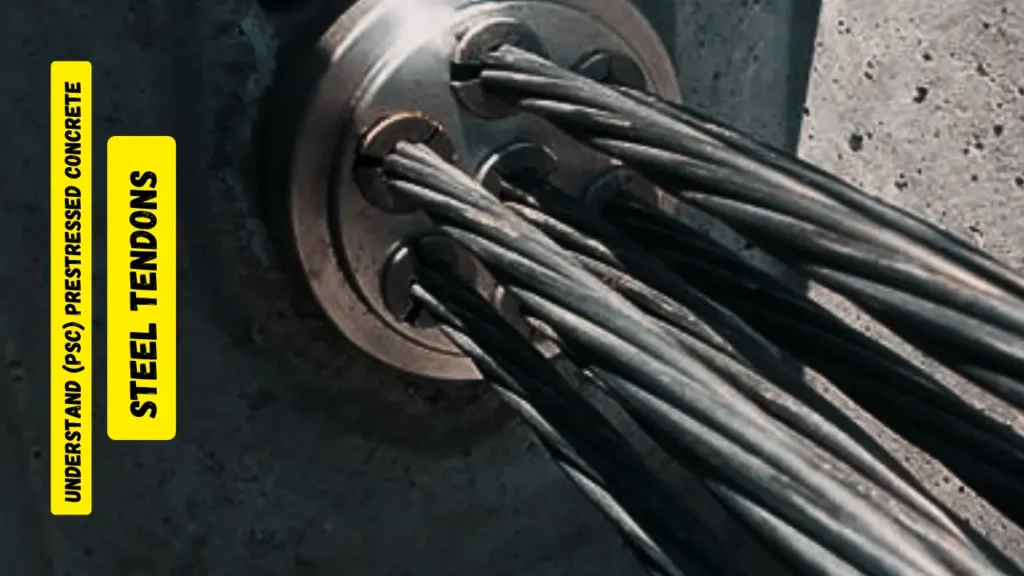

- Concrete: High-strength concrete is used to withstand the high compressive stresses.
- Tendons: High-tensile strength steel tendons are used, which can be in the form of wires, strands, or bars.
- Anchorage Devices: These devices are used to anchor the tendons in place after they have been tensioned.
4. Advantages of PSC
- Increased Load Capacity: Prestressing allows concrete members to carry higher loads and span longer distances.
- Improved Durability: The introduction of compressive stresses reduces the likelihood of cracking, thus enhancing durability.
- Material Efficiency: Prestressed concrete uses materials more efficiently, often reducing the amount of concrete and steel required.
- Design Flexibility: Allows for more innovative and slender designs in architecture and construction.
5. Applications of PSC

Prestressed concrete is widely used in various structural applications, including:
- Bridges and Overpasses: Long spans with minimal supports.
- High-Rise Buildings: Floors, beams, and columns with reduced cross-sections.
- Industrial and Commercial Buildings: Large open spaces with fewer columns.
- Parking Structures: Durable and resilient against heavy loads.
- Marine and Offshore Structures: Resistance to harsh environments.
- Water Retaining Structures: Tanks and reservoirs with high internal pressures.
- Railway Sleepers and Pavements: Enhanced performance under dynamic loads.
6. Design Considerations of PSC
- Load Analysis: Accurate determination of loads, including dead loads, live loads, and environmental loads.
- Stress Calculations: Ensuring that the induced compressive stresses effectively counteract the expected tensile stresses.
- Durability Factors: Considering factors like corrosion resistance and long-term performance.
- Construction Methods: Choosing the appropriate method (pre-tensioning or post-tensioning) based on the project’s requirements.
7. Challenges of PSC
- Complexity: Prestressed concrete requires precise calculations and specialized construction techniques.
- Cost: Initial costs can be higher due to the need for high-strength materials and specialized labor.
- Maintenance: Ensuring the integrity of the prestressing tendons over the structure’s lifespan, particularly in aggressive environments.
Prestressed concrete is a type of concrete in which internal stresses are introduced to counteract the tensile stresses that will be imposed in service. This technique increases the material’s performance and allows for more versatile and efficient structural designs. Here are some common uses of prestressed concrete:
Where mostly use Pre-stressed concrete
1. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Bridges
- Long-Span Bridges: Prestressed concrete is ideal for bridges with long spans as it can handle higher tension and compression forces.
- Overpasses and Underpasses: These structures often require robust materials that can withstand heavy traffic loads.
2. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Buildings
- High-Rise Buildings: Prestressed concrete is used for beams, floors, and columns to provide additional strength and reduce the size of structural elements, which can save space and materials.
- Parking Structures: The durability and load-bearing capacity of prestressed concrete make it suitable for parking garages.
3. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Industrial Structures
- Warehouses: Prestressed concrete slabs and beams are used to create large, open spaces without the need for numerous columns.
- Factories: The material’s strength allows for large bays and open spaces necessary for industrial operations.
4. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Marine Structures
- Docks and Wharves: These structures benefit from the durability and resistance of prestressed concrete against harsh marine environments.
- Offshore Platforms: Prestressed concrete is used in the construction of various offshore structures due to its high strength and resistance to corrosion.
5. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Tanks and Silos
- Water Tanks: Prestressed concrete is used for water storage tanks due to its ability to handle the internal pressure exerted by the stored liquid.
- Grain Silos: The material provides the necessary strength and durability for storing large quantities of grain or other materials.
6. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Railway Sleepers
- Railroad Ties: Prestressed concrete sleepers (ties) are used in railway tracks for their ability to withstand dynamic loads and environmental conditions.
7. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Pavements
- Airport Runways: Prestressed concrete is used in the construction of airport runways for its ability to handle the heavy loads of landing aircraft.
- Highway Pavements: The technique is also applied in highway pavements to enhance durability and reduce maintenance needs.
8. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Water Retaining Structures
- Dams and Reservoirs: Prestressed concrete is used in the construction of dams and reservoirs to ensure they can withstand water pressure and prevent leakage.
9. Pre-stressed concrete Used in Stadiums and Arenas
- Long-Span Roofs: The material is used for long-span roofs in stadiums and arenas, providing large, unobstructed spaces.
Understanding Prestressed Concrete
What is Prestressed Concrete?
Concrete with internal stresses to counteract tensile stresses, improving performance.
🔧
Basic Principle
⚙
Compressive forces counterbalance tensile stresses.
Methods of Prestressing
Pre-tensioning
⚔
Tendons stretched before concrete is poured.
Post-tensioning
⚕
Tendons tensioned after concrete sets.
Components
⚖
Concrete: High-strength
Tendons: High-tensile steel
Anchors: Hold tendons in place
Advantages
💰
Load Capacity: Higher loads
Durability: Less cracking
Efficiency: Less material
Flexibility: Innovative designs
Applications
🚧
Bridges, Buildings, Parking Structures, Marine Structures, Water Tanks, Railway Sleepers, Pavements
Challenges
⚠
Complexity: Precise calculations
Cost: High initial cost
Maintenance: Tendon integrity

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!

