Water is a very important thing that humans need. It is all around us on Earth, but there is only a small amount of water that we can use. We get water from rain and from the ground, and source of water Environmental Engineering, we will learn more about where water comes from. This post will help you understand all of these things better for your studies.
Table of Contents
Surface and subsurface sources of water
The various sources of water are as below:
- Surface sources:
- Streams
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Ponds
- Natural or Artificial reservoirs
- Sub-surface sources:
- Springs
- Infiltration galleries
- Porous pipe galleries
- Wells
- Infiltration wells.
Also Read,
1) WHAT IS FILTRATION | THEORY OF FILTRATION
2) TOWN AND COUNTRY PLANNING: INTRODUCTION AND NOTES
3) AIR POLLUTION – ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING | NOTES
Surface Sources
- Surface sources are also ground surface sources.
- Water can be easily stored, naturally or artificially, on the ground surface.
- This source includes streams, rivers, lakes, pond, artificial reservoirs, stream, etc.
Streams
During the rainy season in mountainous regions, water accumulates at the mountain’s summit and subsequently streams down in the form of flowing watercourses.
The quality of water in streams is normally good to some extent.
Rivers
Several small streams, flowing over from the mountains, combine to form a river.
The river is the only surface source of water that is available in abundance and can be easily used.
Mostly, all the cities situated near the river, discharge their sewage in the river. Nowadays, this has become a major problem for environmental safety.
In India, some rivers are perennial while others dry up in the summer.
Lakes
Source of water In mountains, in some places, natural basins are formed with impervious beds. Water from streams generally moves towards these regions to form a lake.
Generally, water in lakes is of good quality because the water is still undisturbed.
Natural sedimentation takes place.
Lake water is suitable for industrial use.
Ponds
Ponds are depressions in plains; in which water is collected during the rainy season.
Ponds are mostly found in small villages.
Natural or Artificial reservoirs
Reservoirs play a significant role as a primary water source during the summer in India. Their substantial storage capacity allows people to access water during periods of scarcity.
Sub-surface Sources
- These are also known as underground sources. A portion of rainfall infiltrates the ground and gets stored as sub-surface water at the hard stratum.
- Various subterranean sources, including wells, tube wells, springs, infiltration galleries, and porous pipe galleries, form the primary categories of sub-surface water sources.
- These mainly depend on the underground water table, which ultimately depends on the nature of the soil.
- Permeable soil percolates in large quantities which increases the water table.
-
Springs :
- In certain instances, when the groundwater levels are significantly elevated, the water emerges onto the surface through natural springs.
- Due to the presence of sulfur in certain soil, they discharge hot water. The following are the main two types of spring.
(i) Gravity springs: In this case, the underground water level rises, and the water outflows through the sides of the natural valley or depression.
The water table fluctuates regularly and the quantity of water in gravity
springs becomes uncertain. The flow of water may be reduced to zero.
(ii) Artesian Springs: These wells serve as automated sources of pressurized water flow, allowing for the convenient storage of this water in designated tanks.
These are mostly found in hilly regions.
Generally, springs are formed under the following circumstances :
i. When the surface of the earth drops sharply below the normal ground water table.
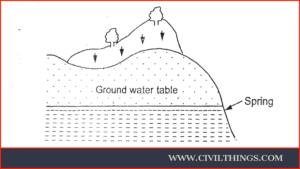
ii. When, due to an obstruction, groundwater is collected in the form of a reservoir and forces the water to overflow at the surface.
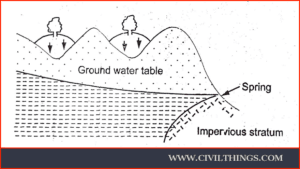
2. Infiltration Galleries:
- Generally, groundwater flows toward ponds or lakes.
- To capture this water, a canal or tunnel can be excavated, incorporating strategically placed.
- apertures at right angles. These subterranean passages are commonly referred to as infiltration galleries.
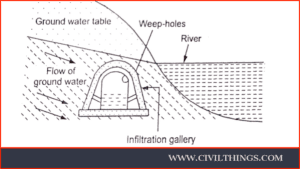
-
Porous Pipe Galleries :
- Where there is a large quantity of groundwater available over a large area, it can be cheaply collected by laying porous pipes.
- These pipes collect and dispose of collected water, and a well is constructed to take out water.
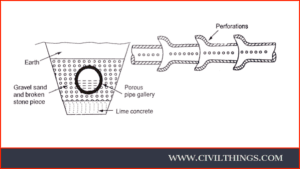
-
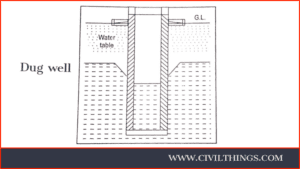
Well:
- A vertical hole dug or drilled under the ground to trap the subsoil water is called a well.
Wells may be shallow or deep. - The wells must be dug a minimum of 20 meters away from the source of communication.
- Wells are classified as :
(i) Dug well, (ii) Driven well, (iii) Tube well
The dimensions of these wells range from 1 meter to 4 meters in diameter, with depths varying between 2 and 9 meters. - They are specifically designed for depths less than 20 meters and are ideal for handling small water discharges.
- The accompanying figure illustrates a dug well.
-
Infiltration well:
- The shallow wells constructed under beds of rivers are called infiltration wells.
- These mechanisms are implemented to enhance the productivity of the well specifically during the summer season.
For more Understanding PDF LINK
Comparison Between Surface & sub-surface sources of water
| Surface Sources | Sub-surface Sources |
| (1) They are in the form of lakes, streams, ponds, rivers, and storage reservoirs.
(2) On occasion, these water sources can be heavily contaminated, posing risks to human health if consumed. They may contain inorganic pollutants and residues from industrial activities. (3) Huge quantity of water is available during monsoon but is considerably reduced during summer. (4) They are to be suitably tested and a line of treatment is to be decided before they are adopted for public use. (5) They are useful for big towns & cities. They can be adopted for irrigation facilities also. | (1) They are in the form of infiltration galleries, infiltration wells, springs, and wells.
(2) They are generally free from impurities because of natural filtration but may contain large amounts of dissolved salts, minerals, and gases. (3) The quantity of water available is generally limited. (4) They can be supplied to the public with no or minor treatment only. (5) They are useful for small towns & villages only.
|

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!

It’s very useful Web sites 😃
Nice job sir🙏⚡
Thanx sir