Air pollution is a major threat to today’s growing world. Every day the rate of air pollution. The atmosphere is getting to a higher rate.

Table of Contents
Our country India ranks eighth for air pollution most air pollution is man- mode Air pollution is increasing due to hazardous gases which have very harmful effects on the human body & life
Air is the first support that all living things need to survive. Because we cannot imagine that there is no air in the environment. Without air, neither we nor any living thing can survive for a lifetime.
Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other air dust, etc., are not easily visible to us in the atmosphere, but these air are separated by special processes. come Hence air is said to be a mixture of different gases, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and various oxides of nitrogen released from the combustion of different fuels.
Harmful factors such as toxic airborne dust, micro-organisms, etc. contaminate the hag. This is called air pollution. This air pollutions have bad effects on all living organisms. We should try to keep our surroundings free from pollution. Due to pollution, we get many types of physical diseases so human life is very dangerous.
Also, Read
1) WHAT IS FILTRATION | THEORY OF FILTRATION
2) TOWN AND COUNTRY PLANNING: INTRODUCTION AND NOTES
Air pollution defines as:
Air pollution is defined as excessive assiduity of foreign country matter in the air which adversely affects the well-being of personnel or causes property damage. It also affects plants, animals, the human body, and buildings.
Source of Air pollution :
-
Natural source of air pollution
-
Man-made source of air pollution
A) Natural source of air pollution

1) Products from atmospheric reaction ( Photochemical)
2) Aerosols – particulates
3) Micro-organisms
4) pollens
4) Radioactive minerals
5) volcanic ash and gases
B) Man-made source of air pollution
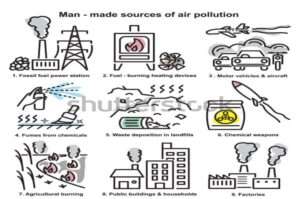
1)Combustion of fuels
2) Industries
3) Thermal power plant
4) Automobiles
5) Agriculture activities
6) Nuclear power plants
Causes of air pollution
A) Natural source of air pollution
- Volcanic Eruption: Eruption releases solid, gaseous, and liquid materials. E.g.Sulfur Dioxide, Carbon Dioxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, Ammonium Chloride, Hydrogen, Vapor, Dust
- Earthquakes: Due to earthquakes, toxic gases and water vapors from the interior of the earth are mixed into the air in large quantities.
- Whirlwinds and dust storms: Dust, debris, soil, pollen, and micro-organisms on the ground are mixed into the air.
- Wildfires: Wildfires release carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and smoke into the atmosphere.
- Microorganisms due to mixing with air: E.g. Spores of some bacteria, and fungi mix with air.
B) Man-made source of air pollution

- Use of Fuels 1. Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and lead compounds are mixed in the air due to the use of coal, wood, LPG, kerosene, diesel, and petrol. II. Open burning of solid waste, agricultural waste, and garden waste causes air pollution.
- Industrialization Huge amount of smoke is emitted from various factories. Sulfur emissions, and nitrogen oxides, mix with the atmosphere.
- Nuclear power generation and nuclear explosion In nuclear power generation, the use of elements such as uranium, thorium, graphite, and plutonium causes air pollution due to radiation.
Classification of air pollution
according to how they are formed they are classified as.
-
Primary air pollution
-
Secondary air pollution
1) Primary air pollutants are those which are emitted directly from identifiable sources.
Eg:
(a) Particulate matter such as dust and aerosols,
(b) Pollens
(c)Sulphur compounds (SO, SO3, H₂S)
d) Nitrogen compounds (NO. NO,, NH,
(e) Carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
(f)Photochemical oxidants
(g) lead
(h)Hydrocarbons
1)Halogen compounds
(Hydrogen fluoride, hydrochloric acid)
2) radioactive materials.
2) Secondary air pollutants: are those which are formed in the atmosphere as a result of interaction between two or more primary air pollutants or by reactions with the normal atmospheric constituents with or without photoactivation. This is more harmful to the human body.
Eg.
- Sulphuric acid
- Ozone
- Formaldehyde
- Peroxy-acetyl-nitrate (PAN)
- Photochemical smog
-Sulphuric acid (H₂SO) is formed by simple chemical reactions combination of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and water (H2O) vapor. It causes acid rain.
-Ozone, peroxy-acetyl nitrate (PAN), etc., are formed by photochemical reactions caused by sunlight between two primary pollutants.
Characteristics of air pollution:
1)Carbon Monoxide (CO): Automobile exhausts are the main contributors to CO. The (CO) causes asphyxia. Eg. loss of consciousness as a result of too small oxygen levels and too much carbon dioxide in the human blood.
2)Sulphur dioxide (SO): It is one of the most important air pollutants and exists where ever fossil fuels are burnt. Thermal plants produce the biggest quantity of SO₂.
3)Hydrocarbons and Photochemical oxidants: Hydrocarbons are mainly released into the atmosphere by automobile exhausts.
4) Oxides of Nitrogen: These are the second most abundant pollutants of air in many cities ranking next to SO, The oxides of nitrogen are produced from air oxidation, electrical discharge, solar radiations, incineration plants, welding operations, etc.
5)Lead: It is mainly injected into the atmosphere from automobile exhausts, particularly by automobiles running on They irritate mucous membranes of the nose, throat, and lungs.

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!
