FORMAL DEFINITION OF AIR POLLUTION
According to the Government’s Air Act of India, 1987, air pollution is defined as air pollution is the presence of all substances, props, and airborne substances i.e. air pollution is harmful to human life, living animals, plants, or property.
Take Perkins’s definition of scientist in 1974 air pollution is an air pollutant in the outdoor environment or more harmful substances or substances such as dust, fumes, odors, fumes and vapors in quantity and characteristics, and duration such as being dangerous to humans, plant or animal life and property. The definition of unreasonably interferes with comfortable enjoyment includes only the outdoor environment and the emissions in the kitchen are noxious air and faulty planning.

Factors affecting human Health.
- Nature Of the pollutants
- The concentration of the pollutants
- Duration OF exposure
- State the health of the receptor
- The age group of the receptor.
Effects Of Air Pollution
- Reduced lung functioning.
- Irritation of eyes, nose mouth & throat
- Asthma attack.
- Repository Symptoms such as coughing and wheezing.
- Increased respiratory disclosure such as. brownies.
- Reduced Headaches and energy levels.
- Headache and dizziness.
- Description of endocrine, reproductive & immune Systems.
- Neuro bebo visual Dixon dead
- Cardiovascular problem
- Cancer.
- Premature death.
Particulate matter effect.
A. Effects of Human Health effect.
- wheezing and coughing.
- Heart attacks and H depth.
- Pollens cause asthma
- cancer
- shortening of lifespan
- genetic defects
- TSP (Total suspended particles)
- In the presence of Son’s direct correlation. bet TSP and hospital visits for bracelet Lashes, emphysema, pneumonia, and Cardiac disease.
- 60,000 deaths from the PM.
- 1% increase in mortality for every 10 mg/m³ increase in PM.
- Respiratory mortality is up. the Same 3.4% For Cardiovascular mortality is up 14%. For the Some.-Heart attacks and H depth.
B) Effects on trees and plants.
- The air pollutants affecting trees and plants are dioxide, hydrogen fluoride, etc.
C) Effects on animals.
- Fluorine, arsenic, or lead may cause contamination of vegetarian food and affect the animals when they eat it.

2) Effects on physical features of the atmosphere.
- Effect on visibility
- effect on atmospheric constituents
- Greenhouse effect
- Ozone layer depletion
- Acid rain
- Global warming
D) Effects on visibility.
- Photochemical and fog smog reduces visibility considerably.
E) Effects on atmospheric constituents.
- Carbon dioxide CO2 is considered before a rise in ambient temperature.
F) Ozone layer depletion.
Cause: This ozone layer acts as an umbrella against the harmful ultraviolet radiation reaching the earth. When chemical pollutants such as chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) are emitted from refrigeration and other Industrial operations. nitrous oxide pollutes the atmosphere and some of the ozone is broken down and resulting in a decrease in ozone concentration in the atmosphere, in a consequence, more ultraviolet radiation reaches the earth.
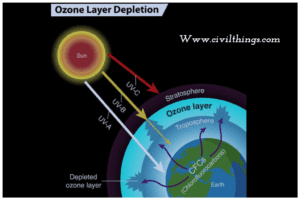
- Damage to the immune system.
- Disturbance in ecosystem
- Effect on crop yield
- Increase of skin eye ailments and skin
- Shorter Life of paints and plastics
Remedy: For protecting the ozone layer, the emission of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) should be restricted.
G) Green-house effects
Effect: if causes an appreciable rise in temperature of the earth’s surface.
Couse: Gases like Conocen de org and chemicals Tkochlorotuarecoton (cic) are responsible for green home elles pictures dioxide CO, is the chief responsible for the Greenhouse effect.
Remedy: The greenhouse effect can be tackled by reducing the rate at which fossil fuels Ske coal is burnt.
H) Acid rain
The rainwater is slightly acidic. The acidity level increases with SO2, NO2, etc. The acidity level in rainwater is caused due to the formation of secondary pollutants such as Were load (H2SO2), nitric acid (HNO3), and falchion acid (HCA) due to the reaction of water vapors with these gases.
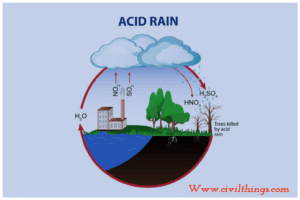
Has been specified that when the pH of the ran wafer is less than or equal to 5 the rain is termed acid rain, 2/3 of acid rain is due to
SO2 is produced mainly by the burning of cool and ol in industries The SO2 pollutant leads to H, SO2 acidity. Another primary pollutant responsible for 1/3 of acid rain is NO2, which is produced mainly by automobile emissions. The NO2 pollutant leads to HNO2, acidity. Acidic fans damage forests, crops, buildings, and monuments (eg: the Taj Mahal monument).
I) Global warming
Global warming is considered to be the outcome of air pollution caused by man-made sources.
2.) Methods of controlling air pollution
- Control of air pollution by zoning.
- Dilution of source discharge by use of a tall stack (Chimney)
- Control by using source correction method ( vice charging raw material, process methods, equipment, etc.
- Reduction of pollutant discharge at source by using controlling equipment.
2.1.) Control of air pollution by zoning
By proper zoning, the city should be planned in such a way that heavy residential areas and Industries are not located too close to each other.
Providing a green belt between the industries and the township will reduce the impact of pollution.
2.2) equipment of control by particle pollutants from the gas stream
- Gravity setting chambers
- Cyclonic separators or cyclones
- Fabric filters
- Electrostatic precipitators
- Scrubbers or wet collectors
Electrostatic precipitators: They utilize electrical energy for the removal of particulate matter from gaseous streams. Particles as small as 0.1 size can be removed by the devices. Generally used to separate 5 as particles from fuel gases in thermal power plant rubber and weight collectors :
Prabhas are devices that utilize a liquid to assist in the removal of particles from the carrying gases stream. Generally, water is used as the scrubbing liquid. Particles less than 0.2 u can also be removed.
Also Check ✅
1. Classification of air pollution

Hi! I’m Sandip, a civil engineer who loves sharing about Civil Engineering & new ideas and tips. My blog helps you learn about engineering in a fun and easy way!

